What is the graphical user interface (GUI)? A Graphical User Interface (GUI) is a visual way for users to interact with computers, applications, and devices using graphical elements such as icons, buttons, and windows instead of text-based commands. It makes computing more accessible and user-friendly, eliminating the need to remember complex command-line instructions.

What is the graphical user interface (GUI)?
In this article, we will explore the components of a GUI, how it works, its key features, disadvantages, different types, and a comparison between the Web User Interface (WUI) and GUI.
What are the five components of the graphical user interface?
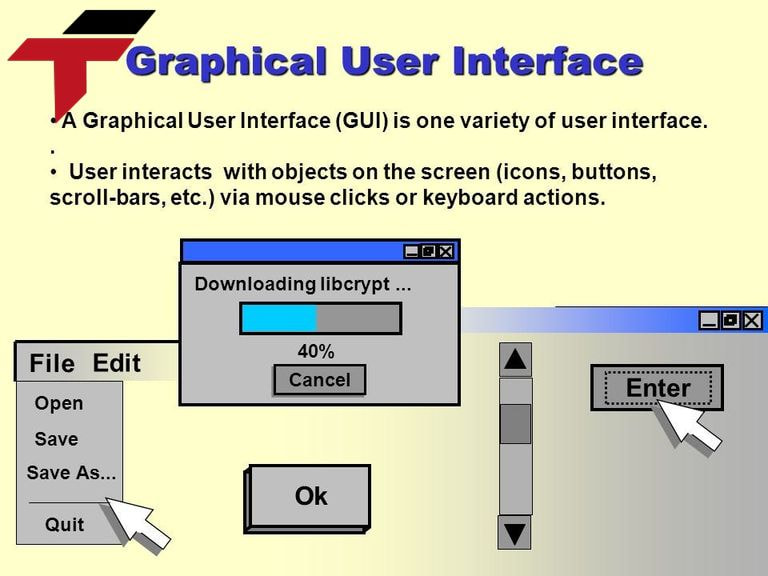
What are the five components of the graphical user interface?
The Graphical User Interface (GUI) consists of five primary components that define its structure and functionality:
- The window is a rectangular area that displays content, allowing users to view and interact with applications. It can contain text, images, buttons, and other UI elements.
- Icons are small graphical representations of applications, files, or functions. They provide an intuitive way to access and execute commands.
- Menus are lists of options presented to the user for easy navigation and function execution. They can be dropdowns, pop-ups, or toolbar-based.
- Buttons: Buttons are interactive elements that allow users to trigger actions, such as submitting a form, closing a window, or saving a file.
- Pointers (Cursors): The pointer, controlled by a mouse or touchpad, is used to select and interact with different elements in the GUI.
How does the GUI work?
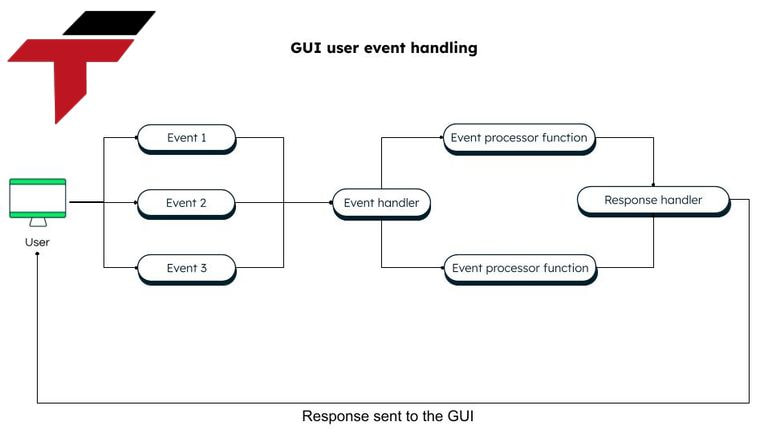
How does the GUI work?
The GUI operates through a combination of hardware and software that enables users to interact with the system visually. Here is how it functions:
- User Input: The user interacts with the GUI using input devices like a mouse, keyboard, touchscreen, or stylus.
- Event Handling: The system detects the user’s actions (e.g., clicking a button, typing text) and processes these events.
- Processing & Interpretation: The GUI translates the user’s actions into commands that the operating system or application understands.
- Response & Display Update: The system updates the display in real time based on the user’s input, such as opening a new window or displaying a pop-up message.
- Feedback Mechanism: The GUI provides visual or auditory feedback (e.g., highlighting a button, or playing a sound) to confirm that an action has been recognized.
What are the salient features of GUI?

What are the salient features of GUI?
Graphical User Interface (GUI) has a friendly interface with many outstanding features to enhance the user experience in the management process, specifically:
- Intuitive representation: GUI sets up intuitive icons and user-friendly interfaces, images and graphics for easy navigation, creating a sense of approachability for users.
- Multitasking ability: The system also allows users to open and manage multiple applications at the same time.
- Drag and drop function: Smooth operations and allows users to move files and components easily.
- Customizable interface: Users can personalize themes, layouts, and shortcuts.
- Accessibility: Includes features such as screen readers, magnifiers, and shortcuts for disabled users.
What are the disadvantages of GUI?
Like other software interfaces, GUIs have many advantages but still have some limitations that users need to be aware of during use:
- Slower performance: Graphics processing can slow down systems with low hardware capabilities.
- Limited control: Some advanced system functions may still require CLI commands.
- Complexity in development: GUI design and development takes a lot of time and effort.
- Security risks: More vulnerable to cyber attacks due to user-friendly access points.
How many types of graphical user interfaces?
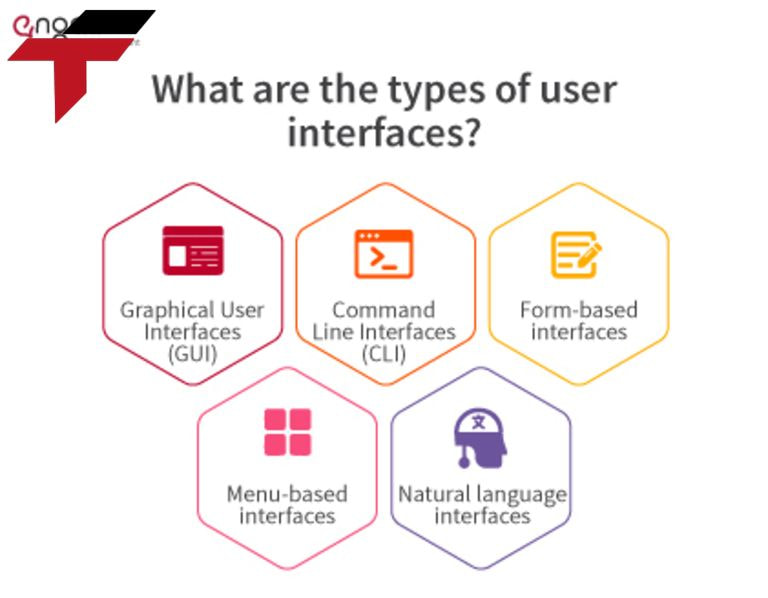
How many types of graphical user interfaces?
Based on its special advantages, Graphical User Interface (GUI) is very popular with customers and is widely used in many different fields. Some popular types of GUI today include:
- Desktop GUI: Appears in operating systems such as Windows, macOS and Linux, helping users easily manipulate software.
- Web-based GUI (Web-based GUI): Used in web applications, browsers and online platforms, optimizing user experience on the Internet.
- Touch GUI (Touchscreen GUI): Appears on smartphones, tablets and service kiosks, allowing direct control by touch.
- Voice-controlled GUI (Voice-activated GUI): Integrated with virtual assistants such as Siri, Google Assistant, and Alexa, helping users perform operations through voice.
- 3D GUI: Used in video games and virtual reality (VR), providing a more vivid and realistic visual experience.
Choosing the right GUI type helps improve the user experience and optimize the performance of the device or application.
What are the differences between the web and graphical user interfaces?
Graphical User Interface (GUI) plays a crucial role in how we interact with digital systems. Two of the most common types are Web Interfaces and Graphical User Interfaces (GUI). While both enhance user experience, they serve different purposes and function in distinct environments.
The table below provides a detailed comparison to help you understand their key differences.
| Feature | Web User Interface (WUI) | Graphical User Interface (GUI) |
| Platform | Runs on web browsers (Chrome, Firefox, Edge, etc.). | Runs on operating systems (Windows, macOS, Linux, etc.). |
| Internet Requirement | Requires an internet connection for access. | Typically does not require an internet connection. |
| Security | Prone to web-based security risks (hacking, phishing, etc.). | More secure when running offline but vulnerable to local threats. |
| Accessibility | Can be accessed from any device with a browser. | Limited to the device where the software is installed. |
| Examples | Google Docs, Facebook, Online Banking Systems. | Adobe Photoshop, Microsoft Word, Windows File Explorer. |
Conclusion
The Graphical User Interface (GUI) has transformed the way users interact with digital systems by making them more intuitive and visually appealing. While it has some disadvantages, its benefits outweigh them, making it the standard for most modern devices. Understanding the different components, working principles, and types of GUIs can help businesses and developers create efficient and user-friendly interfaces for various applications.
