In the era of Industry 4.0, especially in modern industrial automation, programmable logic controllers (PLCs) are indispensable. But what exactly is a PLC and how does it work? Follow this article to the end and you will have the answer. In particular, the article will provide more information about the extremely convenient uses of PLCs in life and distinguish the differences between PLCs and PACs.
What Is a Programmable Logic Controller (PLC)?
What Is a Programmable Logic Controller (PLC)?
The Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) is a specialized computer designed for industrial automation. PLCs are essential in automating specific processes, machine functions, or production lines. These ruggedized computers are adapted to control manufacturing processes like assembly lines, machinery, and robotic devices, offering high reliability.
Besides that PLCs also facilitate data transfer between factory devices enabling real-time monitoring, fault diagnosis, and event management.
In what cases is PLC commonly used?
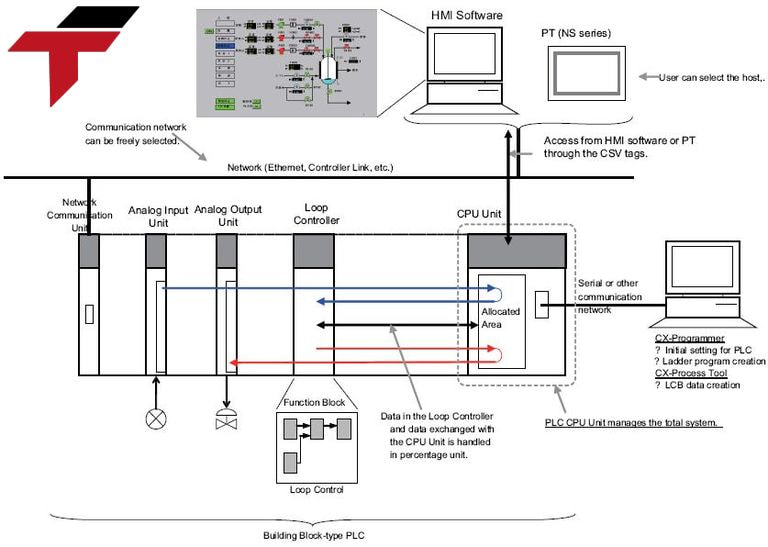
In what cases is PLC commonly used?
PLCs play a crucial role in many aspects of our daily lives such as:
- In life, PLCs control street lighting systems, monitor security cameras and traffic lights, optimize energy usage, and reduce costs while ensuring public safety. They are integral to smart building systems, automating tasks like controlling elevators and lighting. Besides that, you’ll also encounter PLCs in more familiar settings like amusement park rides, automated car washes, and building management systems.
- In the industrial sector, PLCs are employed in numerous processes, controlling complex machinery. They are essential in product assembly, packaging, motion control, and robotics, making them a backbone of modern manufacturing.
What are the parts of PLC?
- Rack: This is considered the physical enclosure that will contain the components of the PLC, to provide a structured mounting system for the modules.
- Power supply: This part helps convert the main power supply into voltage and current suitable for the operation of the PLC according to each scale.
- CPU: The CPU is considered the brain of the PLC, it will be responsible for executing the control program, and at the same time will process input data and generate output signals.
- I/O module: The interface between the PLC and external devices. They can be digital (on/off) or analog (continuous value).
- Programming device: This can be a computer or a handheld device, intended to create, modify, and download programs to the PLC.
How does the PLC work?
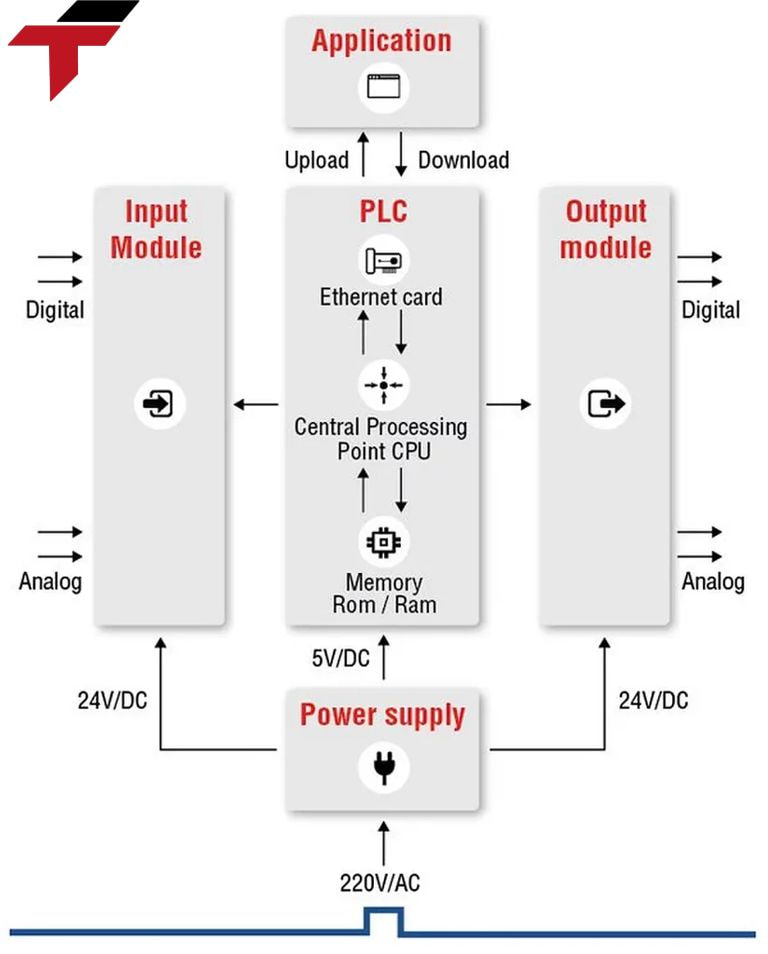
How does the PLC work?
The PLC programmable controller is made up of many different components, but the operating principle is quite simple through the following steps:
- Input scan: The PLC begins by detecting the status of all connected input devices (sensors, switches, buttons). These inputs can range from simple on/off signals to more complex analog data.
- Program scan: This is followed by the execution of the program designed by the engineers. It will help determine the desired state of the output devices.
- Output scan: The PLC controls the output devices, including energizing or de-energizing switches, motor starters, relays, and other mechanical components.
- Clean up: Finally, internal diagnostics and system maintenance are performed, ensuring that the PLC remains operational and responsive to any changes in system requirements.
What are the most common types of PLC?
PLC currently has many different classifications, depending on the characteristics and programming language, there are separate types. However, the two most popular types of PLC that many people know are Fixed PLC and Modules PLC.
- Fixed (Integrated or Compact) PLC: Compact PLCs are often referred to as Fixed I/O PLCs, Both the number and type of inputs and outputs are predetermined by the manufacturer and cannot be modified or expanded.
- Modular PLC: Modular PLCs are more flexible than compact PLCs, allowing users to remove modules from the system and also allowing for the integration of multiple modules, making the system adaptable to a variety of industrial automation requirements.
What is the difference between PLC and PAC?
Similarities: Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) and Programmable Automation Controllers (PACs) are both industrial computers designed for manufacturing environments. These devices act as the central control units for automation processes in industrial settings, managing and coordinating various automation tasks efficiently.
Difference:
| Feature | PLC | PAC |
| Programming ability | Programming is mainly in Ladder Logic language. | Ladder Logic and computer programming languages like C, and C++. |
| Flexibility | Less flexible | Very flexible |
| Stability and durability | Very stable and reliable | Durability equivalent to PLC but with more complex processing capabilities |
| Processing capacity | Limited memory, focus on discrete inputs/outputs. | Larger memory and can handle complex applications |
