Transducers are important devices in measurement and automation systems, converting physical quantities such as temperature, pressure, light or force into electrical signals and vice versa.
As a bridge between the physical and digital worlds, transducers provide high accuracy, stable performance, and diverse applications in industry, medicine, renewable energy, and transportation.
What is a Transducer?
A transducer is a device that converts energy or physical quantity from one form to another. In engineering and automation, transducers play an important role in measurement and control, helping to convert physical quantities (such as temperature, pressure, humidity, light, and sound) into signals that electronic devices or control systems can process.
For example, in an automation system, a transducer can convert the pressure from a pipeline into an electrical signal for a PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) to recognize and take appropriate corrective actions.
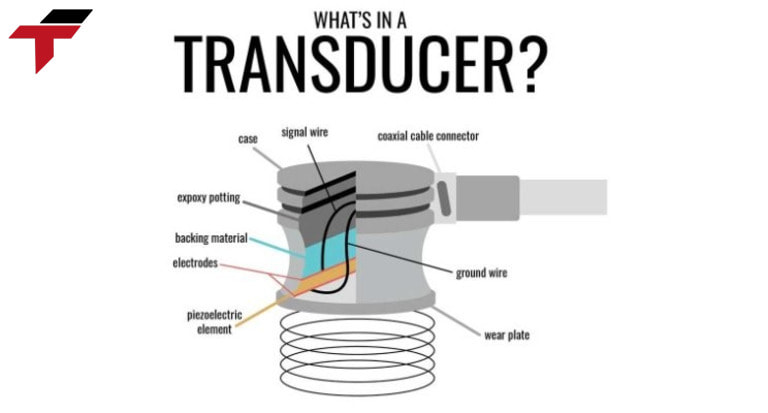
Introduce of Transducer
How many types of transducers are there?
Transducers can be classified into active and passive transducers based on their work and energy use. Here are the details of each type:
Active Transducer
Active transducers are devices that are capable of generating their own output signal without the need for an external energy source. They operate on natural physical principles, such as the thermoelectric, piezoelectric, or magnetoelectric effects. Their output signals are usually weak but can be amplified for use.
- Thermocouple: Converts temperature into voltage using the thermoelectric effect.
- Piezoelectric Transducer: Uses the piezoelectric effect to convert pressure or force into an electrical signal.
- Photovoltaic Cell: Converts light into electrical energy, commonly used in solar power systems.
Passive Transducer
Passive transducers require an external energy source to operate. They do not generate their output signal but rely on a power supply to convert changes in physical quantities into electrical signals. The operating principle often involves changes in electrical properties such as resistance, capacitance or inductance.
- RTD (Resistance Temperature Detector): The resistance of a material changes with temperature, allowing for high-precision temperature measurement.
- LVDT (Linear Variable Differential Transformer): Based on changes in magnetic flux to measure linear displacement.
- Thermistor: Converts temperature changes into resistance changes.
Active transducers are often used in applications that do not require an external power source, while passive transducers are suitable for systems that require high precision and easy control.

Classification of Transducers
What is the difference between a Transducer and a Sensor?
| Characteristics | Transducer | Sensor |
| Definition | A device that converts a physical quantity (temperature, pressure, light, etc.) into another form of energy, usually an electrical signal. | A device that senses or detects changes in a physical quantity in the environment. |
| Function | Converts energy or signals from one form to another. | Sensing or measuring a physical quantity and generating a raw output signal. |
| Role in the system | Output is ready to use in control and measurement systems. | As an input component, providing initial data to the transducer or processing system. |
| Output signal | Electrical signal (analog or digital), easily integrated with electronic devices or systems. | Physical form or parameter change (resistance, capacitance, current, etc.). |
| Scope of use | Wider, including sensor functions. | Narrower, usually focusing on sensing function only. |
| Operating principle | Combines physical and electronic principles to convert energy. | Operates based on changes in the environment (temperature, pressure, light, …). |
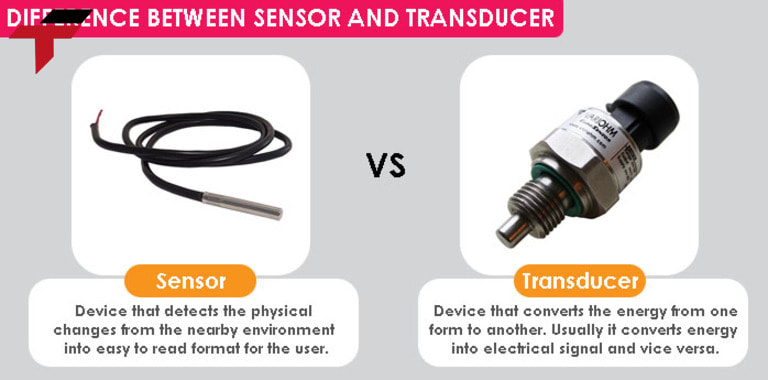
Difference between a Transducer and a Sensor
What are the benefits of a transducer?
- Efficient signal conversion: This allows automation and measurement systems to process and analyze data easily and quickly.
- High accuracy: With modern technology, transducers provide high accuracy when measuring important parameters.
- High integration capability: Transducers can be directly integrated with controllers such as PLC, DCS or SCADA, facilitating the construction of modern automation control systems. This saves time and costs in system design.
- Energy saving: Some transducers, especially active types, do not require an external power source to operate, saving energy and reducing operating costs in long-term applications.
Transducers bring many great benefits, from improving operational efficiency to supporting scientific research and ensuring safety in critical applications.
Notes on using Transducer to ensure accuracy
- Choose the right type of transducer for the application: It is necessary to clearly define the technical requirements such as measurement quantity (temperature, pressure, force), measurement range, and working environment (high temperature, high pressure, or chemical environment) to choose the right type of transducer.
- Ensure proper installation: Correct installation of the transducer’s position and orientation is very important to ensure performance and accuracy. Installation errors can cause incorrect signals or reduce the life of the device.
- Periodic inspection: Transducers need to be regularly inspected and calibrated to ensure accuracy, especially in high-demand applications such as medical or industrial.
- Proper signal processing: Signals from transducers sometimes need to be amplified or filtered to remove noise and increase accuracy. Use signal processors or amplifiers to ensure the signal is clear before entering the system.
Compliance with the above notes not only helps to optimize the performance of the transducer but also prolongs its life and reduces operating costs in the long term.

Things to note when choosing Transducer
Applications of Transducer
- Measurement systems: Transducers are used to measure physical quantities such as temperature, pressure, force, and displacement.
- Automatic control systems: Transducers provide input signals to control systems such as PLCs and DCSs to automate manufacturing processes.
- Medical: Medical ultrasound equipment uses ultrasound transducers to convert sound waves into images to help diagnose diseases.
- Transportation: In the transportation industry, transducers measure oil pressure, engine temperature, and rotational speed to monitor vehicle health. In addition, ultrasonic sensors assist in parking and detect obstacles in modern automobiles.
Transducers are present in almost all areas of life and industry, acting as a bridge between physical factors and technical systems.

Transducers are commonly used in many industries
Conclusion
Transducers are a vital component in many engineering and scientific systems. They allow us to “sense” the world around us by converting different forms of energy into electrical signals that can be measured and processed. Understanding transducers helps us design, build, and operate systems more efficiently.
