Wireless Module has become an important solution in automation systems thanks to its modern wireless data transmission capabilities. With its flexibility, efficiency and ease of integration, this device not only optimizes operations but also saves costs and deployment time. Join FLEXTECH to learn how the Wireless Module helps improve production efficiency and improve management processes in the enterprise.
What is a Wireless Module?
A Wireless Module is a compact device that integrates wireless communication technologies such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Zigbee, LoRa, or NFC. Thanks to its flexibility and efficiency, Wireless Modules have become an important element in modern systems, especially in the Internet of Things (IoT), industrial automation, and smart devices.
The development of Wireless Modules has opened the era of wireless connectivity, helping to optimize communication processes, save costs, and increase operational efficiency in many industries.
What is the structure of a Wireless Module?
A Wireless Module consists of the following 6 main components:
- Microprocessor (MCU – Microcontroller Unit): This is the brain of the module, responsible for processing data, controlling operations and managing communication with peripheral devices.
- Antenna: Used to receive and transmit radio signals, ensuring a stable wireless connection.
- RF (Radio Frequency Transceiver): Converts electrical signals into radio waves and vice versa, allowing wireless communication between devices.
- Communication circuit: Supports connection with other devices via protocols such as UART, SPI, or I2C, helping to transmit data efficiently.
- Power supply: Usually a battery or power supply, providing power for the entire system to operate.
- Memory: Stores data and programs needed to operate the module.
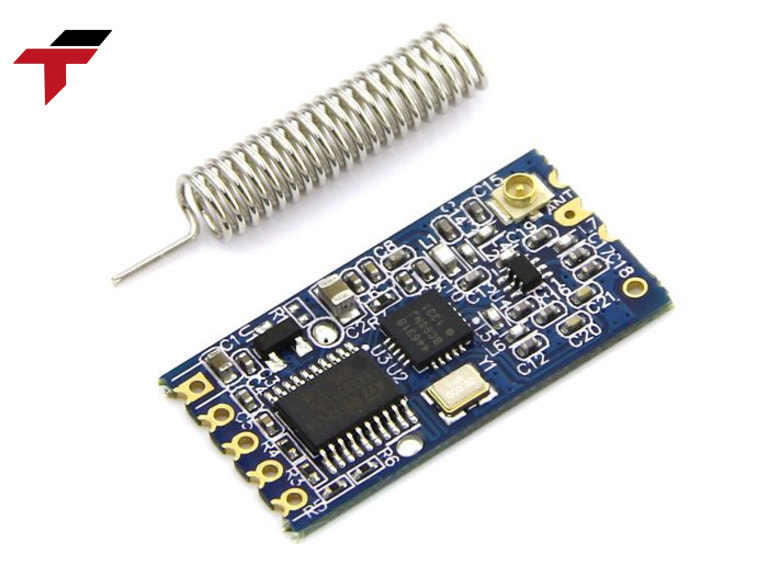
Structure of a Wireless Module
Wireless Module Operating Principle
Wireless Module operates based on the principle of transmitting and receiving signals via radio waves. The operation process includes the following 4 main steps:
Step 1: Signal reception
The module receives radio wave signals from other devices via the antenna. Then the RF receiver decodes the radio wave signals into electronic data.
Step 2: Signal processing
The microprocessor receives the data, analyzes it and performs necessary operations such as encoding, decoding or logic processing. Security algorithms can be applied to encrypt the data before transmitting it.
Step 3: Signal transmission
After processing, the data is transmitted back via the RF transmitter in the form of radio waves. This signal will be sent to the target devices or control systems.
Step 4: Communicate with peripherals
Data from the wireless module can be sent to the microcontroller or computer via communication protocols such as UART, SPI or I2C to perform specific tasks.
Thanks to this operating mechanism, the Wireless Module ensures fast, stable and secure data transmission between devices in the wireless network.
The operating principle of the Wireless Module includes 4 steps
What are the popular wireless connection technologies?
- Wi-Fi: High speed, suitable for applications that need to transmit large amounts of data in a local area network (LAN). For example, security cameras, smart home devices.
- Bluetooth: Low energy consumption, suitable for short-range connections. For example, wireless headphones, smartwatches, health sensors.
- Zigbee: Specialized for industrial or home sensor networks. Supports multiple connection nodes, low energy consumption. For example, smart homes, energy monitoring systems.
- NFC: Near-field connection, often used in electronic payments or data transmission between two devices at very close distances. For example: contactless credit cards, train tickets.
What are the benefits of Wireless Module?
Wireless Module is becoming one of the indispensable technology solutions in modern automation systems.With the ability to transmit data wirelessly and stably, this device not only helps to reduce cabling costs but also increases flexibility in system deployment and maintenance.
Let’s learn about the outstanding benefits that Wireless Module brings to businesses and factories.
- Save costs and installation time: Eliminate the need for complex cabling systems, helping to reduce material costs and installation effort.
- Increase flexibility: Easily change or expand the system without interfering with existing infrastructure.
- Fast and stable data transmission: Applying advanced wireless protocols ensures accurate and efficient information transmission.
- Easy maintenance and monitoring: Supports remote management, helping to quickly detect and handle problems without physical intervention.
- Suitable for many environments: Works well in harsh conditions or difficult to deploy cables, such as hazardous areas or areas with limited space.
With the above benefits, Wireless Module not only improves operating efficiency but is also an important factor in optimizing costs in modern production lines.
Wireless Module helps optimize production
What are the limitations of Wireless Modules?
Despite the significant benefits, Wireless Module still faces some limitations and challenges in its application. Understanding these aspects will help businesses and users optimize the use of wireless technology in the most effective way.
- Relies on the signal: Wireless waves are susceptible to distance, obstacles or environmental interference, leading to connection interruptions. This is especially important when deployed in areas with many buildings or wave-shielding materials such as metal and concrete.
- Security: Data transmitted wirelessly is at risk of being stolen or hacked if not properly protected. Hackers can carry out attacks such as eavesdropping, network intrusion or spreading malware.
- Connection limitations: Some wireless technologies such as Bluetooth have limited operating range, only suitable for short-range connections. This can reduce efficiency when applied in large spaces or distributed environments.
- Power Consumption: Although modern wireless modules have been optimized, some devices still consume a lot of power, especially when transmitting data continuously or in high-interference environments. This can reduce the battery life of devices using the Wireless Module.
What are the common applications of Wireless Module?
Internet of Things (IoT)
Wireless Module is a core component in IoT devices, helping to connect and manage devices remotely over the Internet. For example
- Smart home: Remote control of lights, air conditioners.
- Smart city: Traffic monitoring, energy management.
Industrial automation: In the manufacturing sector, Wireless Module helps monitor and control devices in the production line without complex wiring. This reduces deployment time and improves performance.
Medical devices: A Wireless Module is integrated in medical devices to collect and transmit patient data to the central management system. This helps doctors monitor patients’ health status in real-time, minimize risks, and optimize medical care.
Smart Transportation: In transportation systems, the Wireless Module supports real-time data transmission between vehicles and traffic infrastructure. Applications include:
- Self-driving cars: Positioning and avoiding collisions.
- Traffic management: Reducing congestion with smart sensors and monitoring systems.
Personal devices: Smartphones, smartwatches, and other wearables use Wireless Modules to connect and exchange data quickly. This provides a seamless experience, from syncing health data to streaming music wirelessly.
Wireless Modules are used in a variety of industries
Conclusion
Wireless Module is not only a technological component but also an advanced connection solution, playing an important role in promoting modern industries and life. With the continuous development of technology, The wireless Module promises to continue to bring breakthroughs and improvements in the future.
Hopefully this article has provided you with useful knowledge and helped you make informed decisions for your project.
